Your basket is currently empty!
Hongkonger lead fast-paced lives, with daily work and activities tightly scheduled. To meet these demands, many of us often store various refrigerated fruits, vegetables, and meats in the refrigerator. However, when it comes to retrieving and thawing these refrigerated foods, many people have their own habits. Are these methods appropriate? Correct refrigeration and thawing method not only ensure the freshness and nutrients of food but also effectively extend its shelf life, reducing waste.
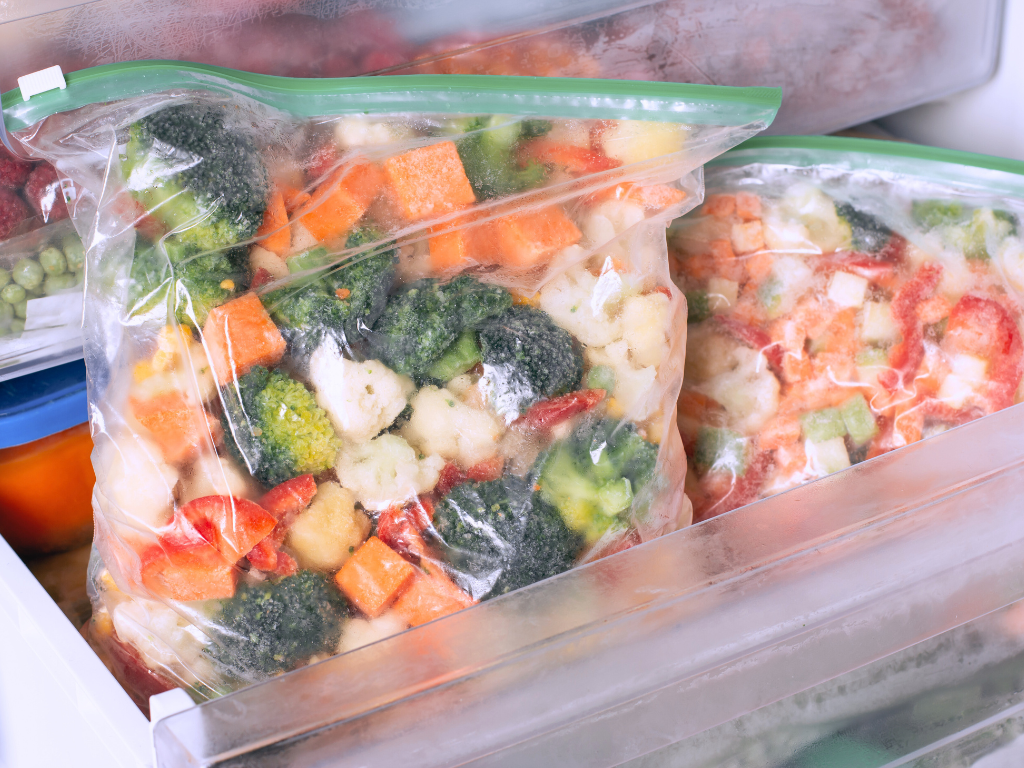

Regarding the Health of Refrigerated Fruits and Vegetables
Fresh fruits and vegetables are indeed more nutritious and complete, retaining the maximum levels of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. However, refrigerated fruits and vegetables also retain nutritional value.
Freezing can effectively maintain most of the nutrients of fruits and vegetables, especially soluble vitamins. Compared to fresh produce, refrigerated fruits and vegetables may slight losses in vitamins and fiber, but overall, the nutritional loss is minimal.
此外,冷藏可以延長蔬果的保質期,減少食物浪費。適當食用冷藏蔬果,仍可獲得豐富的營養。重要的是要注意解凍方法,盡量減少營養流失。
Thawing Methods for Refrigerated Fruits and Vegetables
- Natural Thawing Method: Allow refrigerated fruits and vegetables to naturally thaw at room temperature. This method is gentle and highly recommended as it preserves the nutrients to the fullest, though it may require a longer time. Consider taking them out earlier before leaving the house.
- Refrigerator Thawing Method: Place refrigerated fruits and vegetables in the refrigerator to thaw. This method involves a lower temperature, facilitating slow thawing to maintain nutrients, but it may take several hours.
- Microwave Thawing Method: Use a microwave at low power for a short period to thaw. This method is quick but can lead to localized overheating, causing nutrient loss, so careful operation is necessary.
- Water Thawing Method: Place frozen fruits and vegetables in cold water to thaw. This method is faster but may lead to water-soluble vitamin loss, requiring frequent water changes.
Recommended Refrigeration Storage Times
The actual storage time varies depending on factors such as the type of food, packaging, refrigerator temperature, and other conditions.
Here are some suggestion:
Meats
- Chicken, fish, etc.: Refrigerate for 3-4 months.
- Beef, lamb, etc.: Refrigerate for 6-12 months.
Vegetables
- Most vegetables: Refrigerate for 8-12 months.
- Tender leafy vegetables (e.g., spinach): Refrigerate for 8-12 weeks.
Fruits
- Most fruits: Refrigerate for 8-12 months.
- Citrus fruits: Refrigerate for 2-4 months.
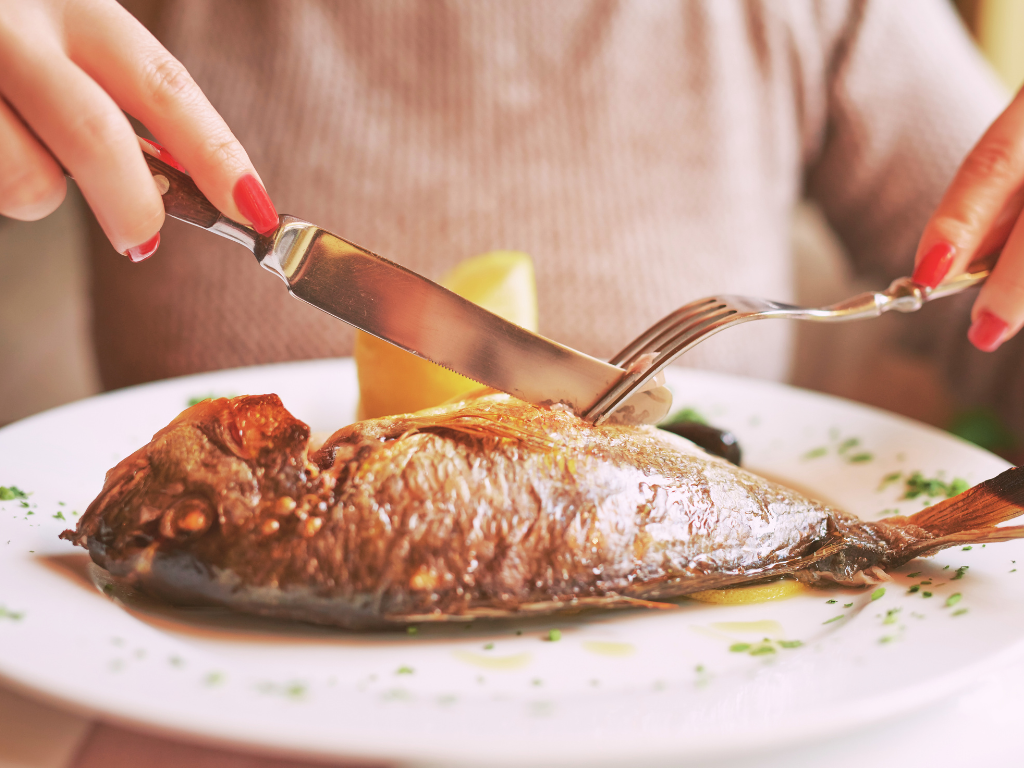
Among various foods, fish is considered more complex due to its perishability, sensitivity to temperature changes, and parasite issues, making it more challenging to handle. Here are some suggestion:
Thawing Methods:
- 冰箱解凍法:將冷藏的魚放在冰箱內緩慢解凍,可以維持較好的質地和營養。這需要4-12小時不等,視魚類的大小而定。
- 冷水解凍法:將魚放入溫度低於21°C的冷水中解凍。這種方法較快,但需要定期更換水以防微生物滋生。
- 微波解凍法:使用微波爐以低功率短時間解凍。這種方法快速,但要小心不要過度加熱造成品質下降。
Storage Methods:
- Refrigeration: Store fresh fish in the refrigerator at temperatures between 0-4°C. It can be kept for 3-5 days.
- Freezing: Place fresh fish in the freezer compartment of the refrigerator or a standalone freezer, maintaining temperatures at -18°C or below. It can be stored for 6 months to 1 year.
- Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum seal fish before refrigerating or freezing to extend its shelf life.
- Pickling or Smoking: Preserve fish using methods such as salting, pickling in vinegar, or smoking. This can also extend the shelf life of the fish.
Ensure cleanliness and hygiene during both thawing and storage processes to prevent cross-contamination.

Hongkonger are known for their busy lifestyles. To minimize food waste, it's common to split ingredients for multiple uses. While this practice reduces waste, it's essential to consider whether each food item is suitable for repeated refrigeration.
Assessing the suitability of multiple refrigerations based on the characteristics of different food items, here are some suggestion:
Perishable Foods (e.g., Fresh Meats, Seafood):
Each refrigeration cycle slightly reduces the shelf life, potentially impacting the quality and nutritional value of the food.
Processed Foods (e.g., Canned Goods, Frozen Foods):
Processed foods that have undergone sterilization or preservation treatments can often withstand multiple refrigerations without significant effects.
Cooked Foods:
Fully cooling cooked foods to room temperature before refrigeration and reheating can often be reused. However, repeated heating may affect the texture and taste of the food.

While Hong Kong people's attitude of food conservation and thriftiness is commendable, prioritizing health is crucial. Stay tuned to EC for more health tips to maintain wellness in our bustling lives through mindful eating.